선형회귀분석 - 중고차 가격에 영향을 미치는 요인 분석
1. 데이터셋 불러오기 및 확인
kaggle에서 제공하는 중고차 데이터셋을 불러옵니다.
여러 변수들의 전처리 과정을 거치고, 선형회귀분석을 통해 중고차 가격에 영향을 미치는 요인을 분석합니다.
데이터출처링크: Kaggle - Used Car Dataset
Used Car Dataset
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
| car_name | 모델명 |
| registration_year | 등록 날짜 |
| insurance_validity | 보험 유효성 |
| fuel_type | 연료 타입 |
| seats | 좌석 수 |
| kms_driven | 총 주행거리 |
| ownership | 소유권 형식 |
| transmission | 변속장치 타입 |
| manufacturing_year | 제작 년도 |
| mileage(kmpl) | 연비 (Kilometers per Liter) |
| engine(cc) | 엔진 (cc) |
| max_power(bhp) | 제동 마력 (Brake horse power = 실제 마력) |
| torque(Nm) | 토크 (Newton meter) => 변수 삭제 |
| price(in lakhs) | 가격 (1 lakh = 100,000 루피) |
import pandas as pd
origin = pd.read_csv("/Used Car Dataset.csv", index_col=0)
1-1 데이터 정보 확인
origin.info()
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
Int64Index: 1553 entries, 0 to 1552
Data columns (total 14 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 car_name 1553 non-null object
1 registration_year 1553 non-null object
2 insurance_validity 1553 non-null object
3 fuel_type 1553 non-null object
4 seats 1553 non-null int64
5 kms_driven 1553 non-null int64
6 ownsership 1553 non-null object
7 transmission 1553 non-null object
8 manufacturing_year 1553 non-null object
9 mileage(kmpl) 1550 non-null float64
10 engine(cc) 1550 non-null float64
11 max_power(bhp) 1550 non-null float64
12 torque(Nm) 1549 non-null float64
13 price(in lakhs) 1553 non-null float64
dtypes: float64(5), int64(2), object(7)
memory usage: 182.0+ KB
1-2 기술통계량 확인
- 기술통계량 확인 결과 정확하게 모든 값이 같은 변수가 있어서 제거 합니다.
- registration_year는 manufacturing_year와의 다중공선성을 고려하여 제거합니다.
- 제거할 변수:
torque(Nm),registration_year
origin.describe(include="all").T
| count | unique | top | freq | mean | std | min | 25% | 50% | 75% | max | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| car_name | 1553 | 925 | 2017 BMW X1 sDrive20d Expedition | 25 | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN |
| registration_year | 1553 | 178 | 2017 | 40 | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN |
| insurance_validity | 1553 | 6 | Comprehensive | 1084 | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN |
| fuel_type | 1553 | 4 | Petrol | 1013 | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN |
| seats | 1553.0 | NaN | NaN | NaN | 91.480361 | 2403.42406 | 4.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 67000.0 |
| kms_driven | 1553.0 | NaN | NaN | NaN | 52841.931101 | 40067.800347 | 620.0 | 30000.0 | 49134.0 | 70000.0 | 810000.0 |
| ownsership | 1553 | 22 | First Owner | 1240 | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN |
| transmission | 1553 | 13 | Manual | 835 | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN |
| manufacturing_year | 1553 | 19 | 2018 | 236 | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN |
| mileage(kmpl) | 1550.0 | NaN | NaN | NaN | 236.927277 | 585.964295 | 7.81 | 16.3425 | 18.9 | 22.0 | 3996.0 |
| engine(cc) | 1550.0 | NaN | NaN | NaN | 14718574440.514194 | 218562947745.450348 | 5.0 | 1197.0 | 1462.0 | 1995.0 | 3258640000000.0 |
| max_power(bhp) | 1550.0 | NaN | NaN | NaN | 14718574440.514194 | 218562947745.450348 | 5.0 | 1197.0 | 1462.0 | 1995.0 | 3258640000000.0 |
| torque(Nm) | 1549.0 | NaN | NaN | NaN | 14239.891543 | 96662.407522 | 5.0 | 400.0 | 1173.0 | 8850.0 | 1464800.0 |
| price(in lakhs) | 1553.0 | NaN | NaN | NaN | 166.141494 | 3478.85509 | 1.0 | 4.66 | 7.14 | 17.0 | 95000.0 |
origin.drop(["max_power(bhp)", "registration_year"], axis=1, inplace=True)
origin.columns
Index(['car_name', 'insurance_validity', 'fuel_type', 'seats', 'kms_driven',
'ownsership', 'transmission', 'manufacturing_year', 'mileage(kmpl)',
'engine(cc)', 'torque(Nm)', 'price(in lakhs)'],
dtype='object')
1-3 데이터 출력 상위 5개
origin.head(5)
| car_name | insurance_validity | fuel_type | seats | kms_driven | ownsership | transmission | manufacturing_year | mileage(kmpl) | engine(cc) | torque(Nm) | price(in lakhs) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 2017 Mercedes-Benz S-Class S400 | Comprehensive | Petrol | 5 | 56000 | First Owner | Automatic | 2017 | 7.81 | 2996.0 | 333.0 | 63.75 |
| 1 | 2020 Nissan Magnite Turbo CVT XV Premium Opt BSVI | Comprehensive | Petrol | 5 | 30615 | First Owner | Automatic | 2020 | 17.40 | 999.0 | 9863.0 | 8.99 |
| 2 | 2018 BMW X1 sDrive 20d xLine | Comprehensive | Diesel | 5 | 24000 | First Owner | Automatic | 2018 | 20.68 | 1995.0 | 188.0 | 23.75 |
| 3 | 2019 Kia Seltos GTX Plus | Comprehensive | Petrol | 5 | 18378 | First Owner | Manual | 2019 | 16.50 | 1353.0 | 13808.0 | 13.56 |
| 4 | 2019 Skoda Superb LK 1.8 TSI AT | Comprehensive | Petrol | 5 | 44900 | First Owner | Automatic | 2019 | 14.67 | 1798.0 | 17746.0 | 24.00 |
1-4 결측치 확인
- 결측치의 갯수가 많지 않고 데이터 분석에 큰 영향을 미치지 않을 것으로 판단하여 제거 했습니다.
print(origin.isnull().sum())
origin.dropna(inplace=True)
car_name 0
insurance_validity 0
fuel_type 0
seats 0
kms_driven 0
ownsership 0
transmission 0
manufacturing_year 0
mileage(kmpl) 3
engine(cc) 3
torque(Nm) 4
price(in lakhs) 0
dtype: int64
1-5 중복값 확인
- 다수의 중복된 중복된 값이 존재하였으므로 제거 합니다.
print(origin.duplicated().sum())
origin = origin.drop_duplicates(subset=origin.columns, ignore_index=True, keep="first")
420
1-6 변수명 변경
- torque 변수의 값들은 실제 bhp 변수의 값이므로 변수명 변경
origin.rename(
columns={
"ownsership": "ownership",
"mileage(kmpl)": "mileage",
"engine(cc)": "engine",
"torque(Nm)": "bhp",
"price(in lakhs)": "price",
},
inplace=True,
)
1-7 카테고리, 수치형 데이터 및 타겟 데이터 분류
-
manufacturing_year
- 시간에 따라 의존 변수가 선형적으로 변화하고 자동차의 가치가 매년 일정 비율로 감소한다고 가정하여, 년도를 수치형 변수로 사용하였습니다.
-
seats
- 좌석 수의 증가가 특정 변수(차량 가격)에 미치는지를 분석하기 위해 수치형 변수로 사용하였습니다.
categories = [
"insurance_validity",
"fuel_type",
"ownership",
"transmission",
]
num_features = [
"kms_driven",
"mileage",
"engine",
"bhp",
"manufacturing_year",
"seats",
]
target = "price"
2. 탐색적 데이터 분석 및 데이터 전처리
2-1 ownership 변수의 값 정리
- ownership 변수에 맞지 않는 여러 값들이 발견되어 정리 합니다.
origin = origin.loc[
origin["ownership"].isin(["First Owner", "Second Owner", "Third Owner"])
]
2-2 명목형 변수와 수치형 변수 타입 지정
for category in categories:
origin[category] = origin[category].astype("category")
origin["manufacturing_year"] = origin["manufacturing_year"].astype(int)
2-3 df변수에 1차 전처리된 origin 데이터 카피
df = origin.copy()
df.info()
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
Int64Index: 1103 entries, 0 to 1128
Data columns (total 12 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 car_name 1103 non-null object
1 insurance_validity 1103 non-null category
2 fuel_type 1103 non-null category
3 seats 1103 non-null int64
4 kms_driven 1103 non-null int64
5 ownership 1103 non-null category
6 transmission 1103 non-null category
7 manufacturing_year 1103 non-null int64
8 mileage 1103 non-null float64
9 engine 1103 non-null float64
10 bhp 1103 non-null float64
11 price 1103 non-null float64
dtypes: category(4), float64(4), int64(3), object(1)
memory usage: 82.4+ KB
2-4 수치형 변수 boxplot 그래프로 이상치 확인
- engine, max_power, price 등에서 다수의 이상치가 관측 되었습니다.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
features = ["kms_driven", "mileage", "engine", "bhp", "price"]
fig, axes = plt.subplots(3, 2, figsize=(13, 13), dpi=100)
for feature, ax in zip(features, axes.flatten()):
sns.boxplot(data=df, y=feature, ax=ax)
ax.grid(True)
fig.delaxes(axes[2, 1])
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
plt.close()
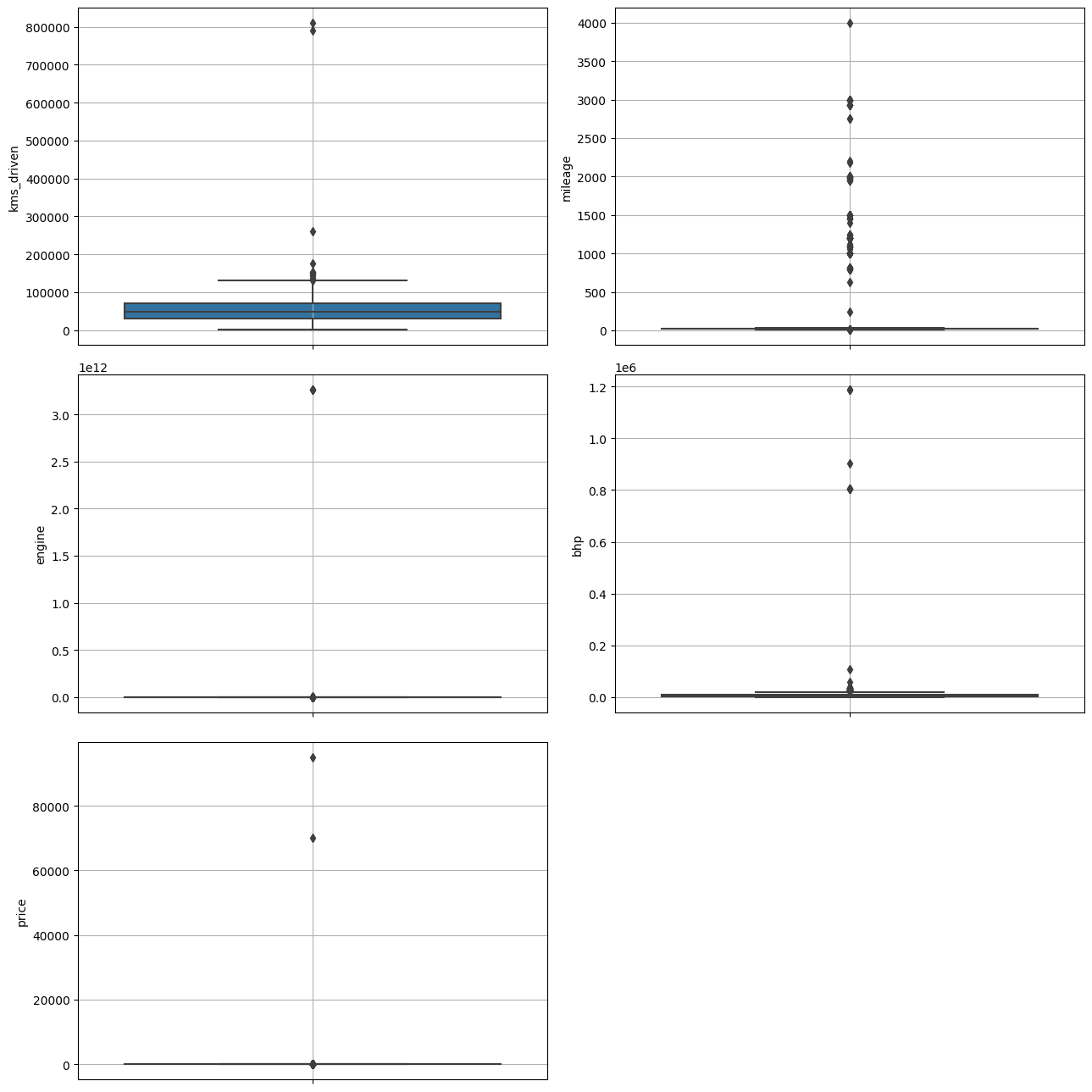
2-5. mileage(연비) 변수에 대한 이상치 확인 및 제거
- mileage값이 28.4에서 245.59로 급격하게 증가하는 이상치가 관측 되어 제거 합니다.
result = df.loc[df["mileage"] > 30, features].sort_values("mileage", ascending=False)
print(f"검색된 값: {result.shape[0]}")
df.drop(result.index, inplace=True)
검색된 값: 134
2-6. bhp(제동마력) 변수에 대한 이상치 확인 및 제거
-
bhp의 단위가 이상할 정도로 큰 값들이 존재하여, 실제 차량 데이터와 비교해본 결과 실제 값으로 확인 되었고 단지 단위가 잘못 표기된 것으로 판단되어 전처리 과정을 거쳐 사용가능한 값으로 변환 하였습니다. (예 : 1186600 = 118.66)
-
2018 Mercedes-Benz S-Class Maybach S500 이상의 값들을 순차적으로 전처리 하였습니다.
thresholds = [460, 460, 600, 600]
for threshold in thresholds:
df["bhp"] = df["bhp"].apply(lambda x: x / 10 if x > threshold else x)
result = df.loc[df["bhp"] > threshold, features].sort_values("bhp", ascending=False)
print(f"검색된 값: {result.shape[0]}")
검색된 값: 455
검색된 값: 11
검색된 값: 9
검색된 값: 0
2-7. price(가격) 변수에 대한 이상치 확인 및 제거
- 가격이 95000으로 기록된 이상치는 제거 합니다.
result = df.loc[df["price"] > 100, features].sort_values("price", ascending=False)
print(f"검색된 값: {result.shape[0]}")
result = df.loc[df["price"] > 100]
df.drop(result.index, inplace=True)
검색된 값: 1
2-7-1. 파생변수 생성하여 brand별 price 분포 확인
df["brand"] = df["car_name"].apply(lambda x: x.split(" ")[1])
df["brand"].unique()
array(['Mercedes-Benz', 'Nissan', 'BMW', 'Kia', 'Skoda', 'Honda',
'Hyundai', 'Tata', 'Renault', 'Ford', 'Jeep', 'MG', 'Maruti',
'Audi', 'Toyota', 'Jaguar', 'Volkswagen', 'Mahindra', 'Land',
'Volvo', 'Isuzu', 'Mitsubishi', 'Porsche', 'Datsun', 'Lexus',
'Mini', 'Fiat'], dtype=object)
plt.figure(figsize=(25, 10), dpi=200)
sns.boxplot(data=df, x="brand", y="price")
plt.grid()
plt.tight_layout()
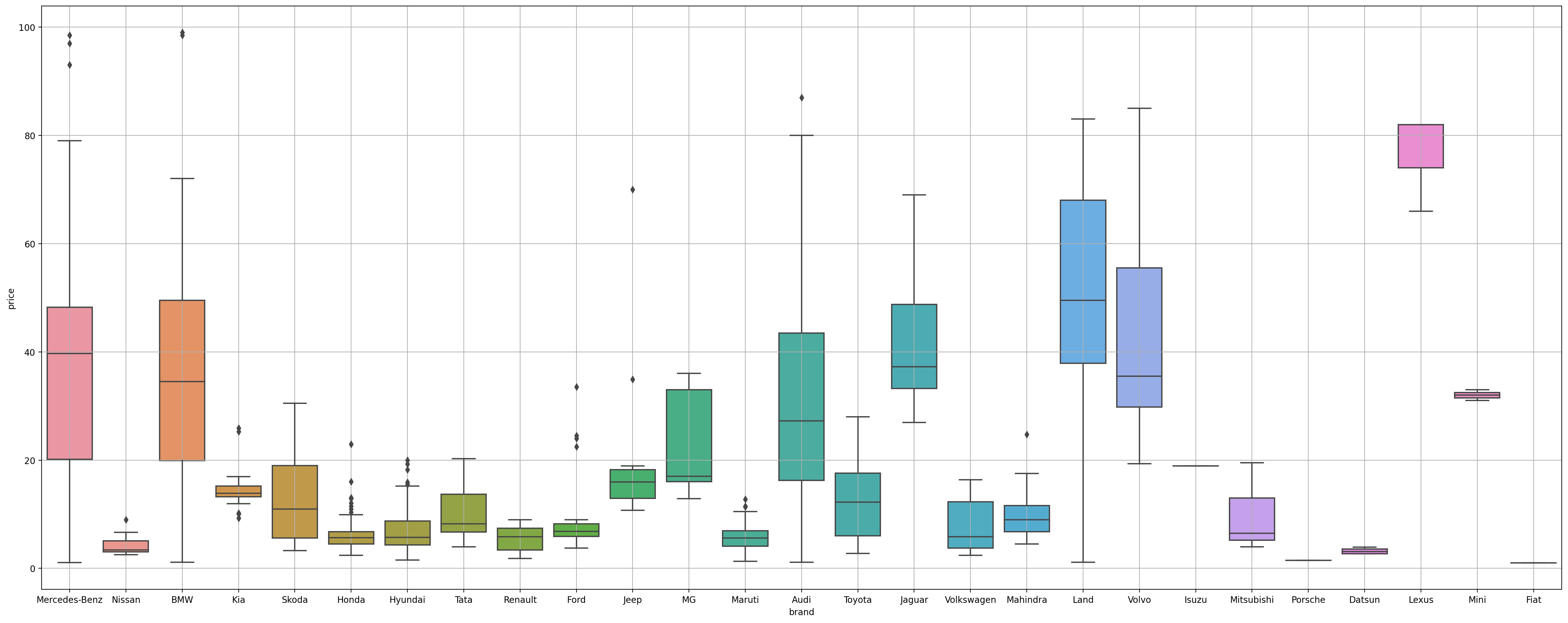
상위 5개 브랜드에서 가격이 비정상적으로 낮은(5 lakhs 이하) 데이터 제거 합니다.
result = df.loc[
(
(df["car_name"].str.contains("benz", case=False))
| (df["car_name"].str.contains("bmw", case=False))
| (df["car_name"].str.contains("audi", case=False))
| (df["car_name"].str.contains("Land", case=False))
| (df["car_name"].str.contains("Jaguar", case=False))
)
& (df["price"] < 5),
["car_name"] + num_features + [target],
].sort_values("price", ascending=False)
df.drop(result.index, inplace=True)
2-8. 자동차 브랜드별 평균 가격을 파생변수로 생성
df["car_name_mean_price"] = df.groupby("brand")["price"].transform("mean")
2-9. kms_driven(주행거리) 변수에 대한 이상치 확인
- 79만km와 81만km는 실제로 관측될 수 있는 수치이긴 하지만, 다른 차량 대비 지나치게 높은 값으로 결과의 신뢰성을 고려하여 이상치로 판단하고 제거 합니다.
df.drop(df[df["kms_driven"] > 700000].index, inplace=True)
2-10. engine(cc) 변수에 대한 이상치 확인 및 제거
df.loc[df["car_name"] == "2014 Mercedes-Benz S-Class S 500 L", "engine"] = 4663
2-11. 수치형 변수 boxplot으로 이상치 재확인
features = ["kms_driven", "mileage", "engine", "bhp", "price"]
fig, axes = plt.subplots(3, 2, figsize=(13, 13), dpi=100)
for feature, ax in zip(features, axes.flatten()):
sns.boxplot(data=df, y=feature, ax=ax)
ax.grid(True)
fig.delaxes(axes[2, 1])
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
plt.close()
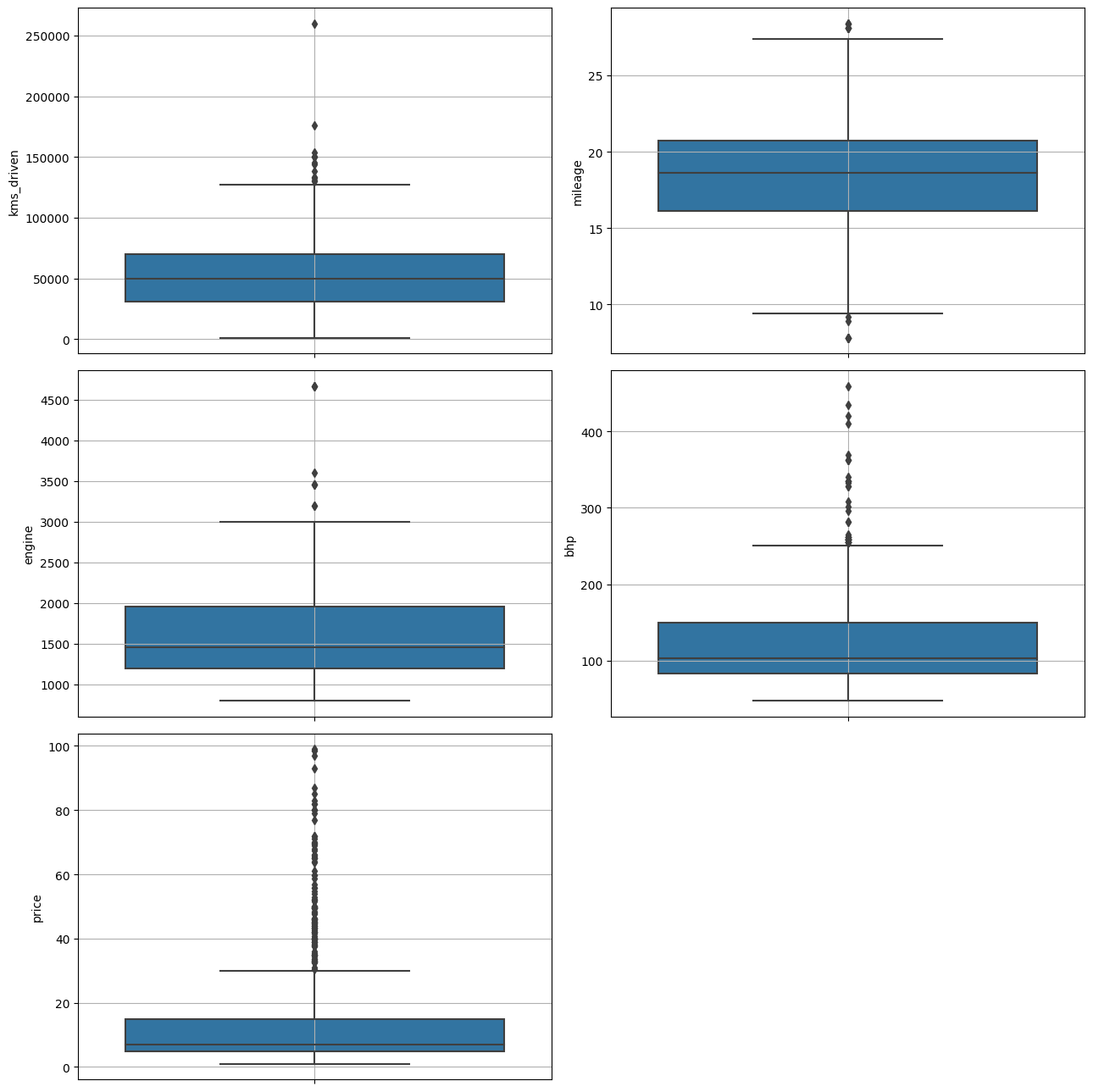
3. 선형회귀분석
num_features.pop(num_features.index("manufacturing_year"))
'manufacturing_year'
3-1. 히트맵 상관관계 확인
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 8), dpi=100)
sns.heatmap(
df[num_features].join(df[target]).corr(),
annot=True,
cmap="coolwarm",
fmt=".2f",
annot_kws={"fontsize": 15},
)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
plt.close()
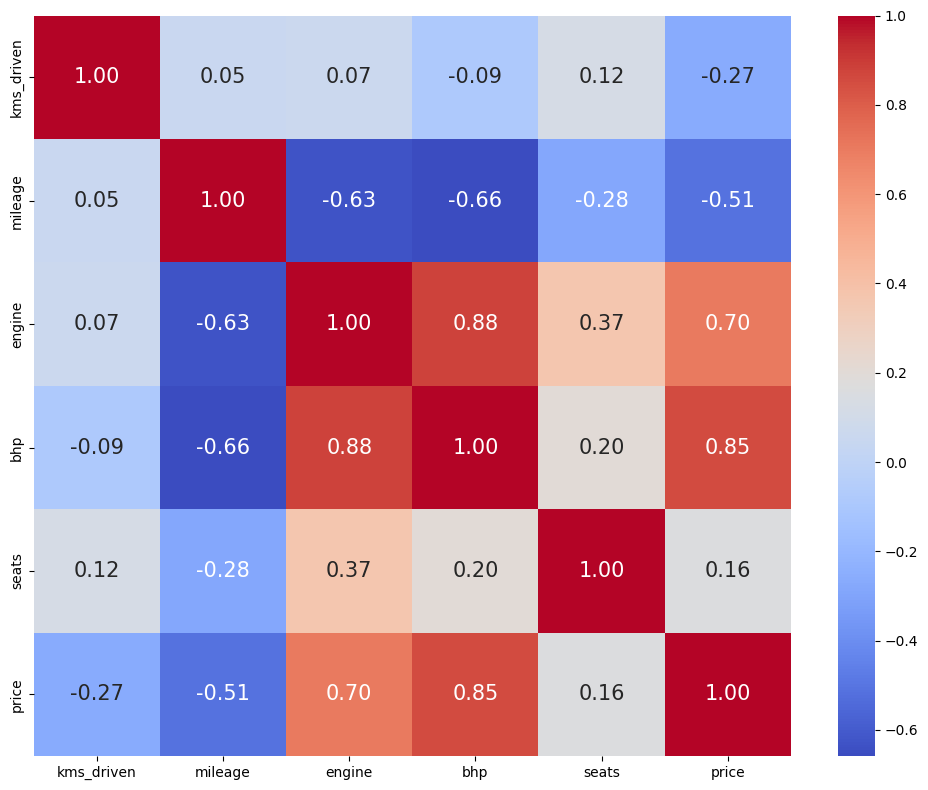
engine과 bhp에서 price와의 강한 양의 상관관계가 관측되었고, mileage와 price의 음의 상관관계가 관측되었습니다.
분석에 사용하지 않을 변수 제거
df.drop(["car_name", "brand"], axis=1, inplace=True)
카테고리 변수 확인
for i in categories:
print(i, df[i].unique(), end="\n\n")
print("=" * 100, end="\n\n")
insurance_validity ['Comprehensive', 'Third Party insurance', 'Zero Dep', 'Third Party']
Categories (4, object): ['Comprehensive', 'Third Party', 'Third Party insurance', 'Zero Dep']
====================================================================================================
fuel_type ['Petrol', 'Diesel', 'CNG']
Categories (3, object): ['CNG', 'Diesel', 'Petrol']
====================================================================================================
ownership ['First Owner', 'Second Owner', 'Third Owner']
Categories (3, object): ['First Owner', 'Second Owner', 'Third Owner']
====================================================================================================
transmission ['Automatic', 'Manual']
Categories (2, object): ['Automatic', 'Manual']
====================================================================================================
df.dtypes
insurance_validity category
fuel_type category
seats int64
kms_driven int64
ownership category
transmission category
manufacturing_year int64
mileage float64
engine float64
bhp float64
price float64
car_name_mean_price float64
dtype: object
3-2. 카테고리 변수 더미화
df = pd.get_dummies(df, columns=categories, drop_first=True)
3-3. 수치형 변수 스케일링
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
scaler = StandardScaler()
num_features_extended = num_features + ["manufacturing_year"] + ["car_name_mean_price"]
df[num_features_extended] = scaler.fit_transform(df[num_features_extended])
3-4. 데이터셋 분리
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
df.drop(target, axis=1), df[target], test_size=0.2, random_state=42
)
x_train.shape, x_test.shape, y_train.shape, y_test.shape
((764, 15), (192, 15), (764,), (192,))
3-5. 다중공선성 확인 및 제거
VIF값이 10 이상인 변수를 제거 합니다
from statsmodels.stats.outliers_influence import variance_inflation_factor
from statsmodels.tools.tools import add_constant
df_with_const = add_constant(df)
vif = pd.DataFrame()
vif["Features"] = df_with_const.columns
vif["VIF"] = [
variance_inflation_factor(df_with_const.values, i)
for i in range(df_with_const.shape[1])
]
vif = (
vif[vif["Features"] != "const"]
.sort_values("VIF", ascending=False)
.reset_index(drop=True)
)
vif[vif["VIF"] > 10]
| Features | VIF | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | fuel_type_Petrol | 29.806683 |
| 1 | fuel_type_Diesel | 28.621752 |
| 2 | bhp | 10.949257 |
df.drop(["fuel_type_Petrol", "bhp"], axis=1, inplace=True)
3-6. 선형회귀분석
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
lr = LinearRegression()
lr.fit(x_train, y_train)
y_train_pred = lr.predict(x_train)
y_test_pred = lr.predict(x_test)
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error, r2_score
print(f"Train RMSE: {mean_squared_error(y_train, y_train_pred):.2f}")
print(f"Test RMSE: {mean_squared_error(y_test, y_test_pred):.2f}")
print(f"Train R2: {r2_score(y_train, y_train_pred):.2f}")
print(f"Test R2: {r2_score(y_test, y_test_pred):.2f}")
Train RMSE: 46.44
Test RMSE: 58.93
Train R2: 0.83
Test R2: 0.82
많은 이상치와 중복데이터 그리고 결측치 등 데이터셋이 클린하지 않아서 전처리 과정에 많은 시간이 소요되었습니다.
그러나 선형회귀분석 결과는 Train RMSE: 46.44, Test RMSE: 58.93, Train R2: 0.83, Test R2: 0.82로 나쁘지 않은 결과를 보여줍니다.





Leave a comment